Kiribati 2001
The new head of state abandoned the privatization policy implemented by his predecessors and announced in mid-1995 that public servants would have their salaries increased. In foreign policy, the Tito government criticized Japan for its passage of the sea around Kiribati with ships with nuclear waste, and at the same time France was criticized for its nuclear tests.
The government planned a balanced budget for 1996, but at the same time saw an increase in government spending of 1.7%. Parts of the funds came from a reserve fund that had been set up to collect payment in accordance with the Danish National Bank. the phosphate extraction at Banaba. The same year, the country entered into a trade agreement with China, with the aim of increasing trade between the two countries.
- Abbreviationfinder: lists typical abbreviations and country overview of Kiribati, including bordering countries, geography, history, politics, and economics.
In December, the Conference of an Independent and Atomic Pacific in Fiji was held. Tito here endorsed the host country’s proposal for a total ban on nuclear testing around the world.
In August 1997 Kiribati signed a friendship agreement with Tuvalu. In September, the Japanese government decided to allocate $ 40 million to build the port of Betio, one of Kiribati’s most important.
Due to the low altitude of the islands, the greenhouse effect and the rise in the seas have caused both government and the population serious concern in recent years. The long-term development will be disastrous for the country.
Kiribati joined the UN in 1999 and the following year in the ILO.
Population 2001
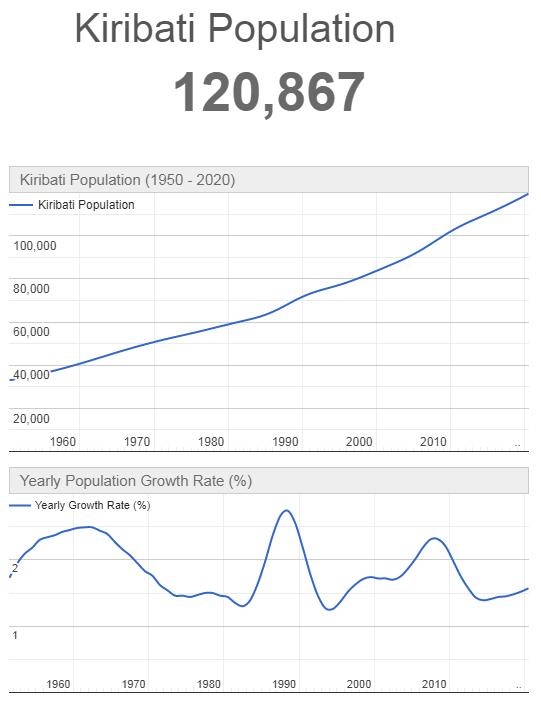
According to Countryaah, the population of Kiribati in 2001 was 92,214, ranking number 199 in the world. The population growth rate was 1.810% yearly, and the population density was 113.9815 people per km2.